RDBMS stands for Relational
Database Management System. RDBMS data is structured in database tables, fields
and records(table rows). Each RDBMS table consists of database table rows. Each database
table row consists of one or more database table fields.
RDBMS store the data into collection of tables, which might be related by common fields (database table columns). RDBMS also provide relational operators to manipulate the data stored into the database tables. Most RDBMS use SQL as database query language.
RDBMS store the data into collection of tables, which might be related by common fields (database table columns). RDBMS also provide relational operators to manipulate the data stored into the database tables. Most RDBMS use SQL as database query language.
2.
What is
normalization?
Normalization
Normalization is the process of simplifying the relationship between data elements in a record. 1st normal form, 2nd normal form, 3rd normal form
Normalization is the process of simplifying the relationship between data elements in a record. 1st normal form, 2nd normal form, 3rd normal form
3.
What are different
normalization forms?
(i) 1st normal form: - 1st N.F is
achieved when all repeating groups are removed, and P.K should be defined. big
table is broken into many small tables, such that each table has a primary key.
(ii) 2nd normal form: - Eliminate any non-full dependence of data item on record keys. I.e. The columns in a table which is not completely dependent on the primary key are taken to a separate table.
(ii) 2nd normal form: - Eliminate any non-full dependence of data item on record keys. I.e. The columns in a table which is not completely dependent on the primary key are taken to a separate table.
(iii) 3rd normal form: - Eliminate any transitive dependence of data items on P.K’s. i.e. Removes Transitive dependency. Ie If A is the primary key in a table. B & C are columns in the same table. Suppose C depends only on B and B depends on A. Then C does not depend directly on primary key. So remove C from the table to a look up table.
4.
What is Stored
Procedure?
Stored procedures are set of Structured Query
Language (SQL) statements that perform particular task.
• SP have repeatedly using data. It helps to reuse the code.
• SP is reduces the complexity of code in code behind.
• SP increase the security to application, it protect from Sql injection and hacking.
• Code maintenance and changes are done very easily. Instead of changing the code in code behind if changes required.
• SP have repeatedly using data. It helps to reuse the code.
• SP is reduces the complexity of code in code behind.
• SP increase the security to application, it protect from Sql injection and hacking.
• Code maintenance and changes are done very easily. Instead of changing the code in code behind if changes required.
5.
What is Trigger?
A trigger is a set of statements
that gets executed implicitly or automatically whenever any one of the
following operation takes place on the table for which trigger has been created
:
1. Inserting record(s) to the table
2. Deleting record(s) from the table
3. Updating the table
1. Inserting record(s) to the table
2. Deleting record(s) from the table
3. Updating the table
6.
What is View?
The SQL view is, in
essence, a virtual table. It does not physically exist. Rather, it is created
by a query joining one or more table.
7.
What is Index?
Indexing is a data structure technique which allows you to quickly retrieve records from a database file. An Index is a small table having only two columns. The first column comprises a copy of the primary or candidate key of a table. Its second column contains a set of pointers for holding the address of the disk block where that specific key value stored.
An index is like a set of
pointers to specific rows in a table.
database indexes help speed up retrieval of data.
What
is cursor?
A SQL cursor is a database object that is used to retrieve data from a result set one row at a time. A SQL cursor is used when the data needs to be updated row by row.
In other word, Cursor
is a database object used by applications to manipulate data in a set on a
row-by-row basis, its like recordset in the ASP and visual basic.
9.
How to implement
one-to-one, one-to-many and many-to-many relationships while designing tables?
One-to-one: Use a foreign key to the referenced table:student: student_id, first_name, last_name, address_id
address: address_id, address, city, zipcode, student_idOne-to-many: Use a foreign key on the many side of the relationship linking back to the "one" side: teachers: teacher_id, first_name, last_name # the "one" side
classes: class_id, class_name, teacher_id # the "many" sideMany-to-many: Use a junction table: student: student_id, first_name, last_name
classes: class_id, name, teacher_id
student_classes: class_id, student_id # the junction table |
10.
What is a NOLOCK?
11.
What is difference between DELETE & TRUNCATE commands?
TRUNCATE TABLE
table_name
DELETE FROM
table_name
DELETE FROM
table_name WHERE example_column_id IN (1,2,3)
| Delete | Truncate |
|---|---|
| The DELETE command is used to delete specified rows(one or more). | While this command is used to delete all the rows from a table. |
| It is a DML(Data Manipulation Language) command. | While it is a DDL(Data Definition Language) command. |
| There may be a WHERE clause in the DELETE command in order to filter the records. | While there may not be WHERE clause in the TRUNCATE command. |
12.
Difference
between Function and Stored Procedure?
Basic Difference
1.
Function
must return a value but in Stored Procedure it is optional( Procedure can
return zero or n values).
2.
Functions
can have only input parameters for it whereas Procedures can have input/output
parameters .
3.
Functions
can be called from Procedure whereas Procedures cannot be called from Function.
Advance Difference
Procedure
allows SELECT as well as DML(INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE) statement in it whereas
Function allows only SELECT statement in it.
13.
When is the use of UPDATE_STATISTICS command?
This
command is basically used when a large processing of data has occurred. If a
large amount of deletions any modification or Bulk Copy into the tables has
occurred, it has to update the indexes to take these changes into account.
UPDATE_STATISTICS updates the indexes on these tables accordingly.
14.
What types of Joins are possible with Sql Server?
Types
of joins: INNER JOINs, OUTER JOINs, CROSS JOINs.
OUTER JOINs are further classified as LEFT OUTER JOINS, RIGHT OUTER JOINS and FULL OUTER JOINS.
OUTER JOINs are further classified as LEFT OUTER JOINS, RIGHT OUTER JOINS and FULL OUTER JOINS.
15. The Different Types of Joins in SQL Server
1.
Self Join
2.Inner Join
3.Outer Join
2.Inner Join
3.Outer Join
3.1. Right Outer Join
3.2. Left Outer Join
3.2. Left Outer Join
3.3 Full Outer Join
4.Cross
join
16.
What is
the difference between a HAVING CLAUSE and a WHERE CLAUSE?
Where Clause:
1.Where Clause can be used other than Select statement also
2.Where applies to each and single row
3.In where clause the data that fetched from memory according
to condition
4.Where is used before GROUP BY clause
Ex:Using Condition for the data in the memory.
Having Clause:
1.Having is used only with the SELECT statement.
2.Having applies to summarized rows (summarized with GROUP BY)
3.In having the completed data firstly fetched and then separated according to condition.
4.HAVING clause is used to impose condition on GROUP Function and is used after GROUP BY clause in the query
Ex: when using the avg function and then filter the data like ava(Sales)>0
1.Where Clause can be used other than Select statement also
2.Where applies to each and single row
3.In where clause the data that fetched from memory according
to condition
4.Where is used before GROUP BY clause
Ex:Using Condition for the data in the memory.
Having Clause:
1.Having is used only with the SELECT statement.
2.Having applies to summarized rows (summarized with GROUP BY)
3.In having the completed data firstly fetched and then separated according to condition.
4.HAVING clause is used to impose condition on GROUP Function and is used after GROUP BY clause in the query
Ex: when using the avg function and then filter the data like ava(Sales)>0
17.
What is
sub-query? Explain properties of sub-query.
A subquery is a query
within a query.
Properties
of Sub-Query
·
A
sub-query must be enclosed in the parenthesis.
·
A
sub-query must be put in the right hand of the comparison operator.
·
A
sub-query cannot contain an ORDER-BY clause.
18. What are types of sub-queries?
·
Predicate
Subqueries - extended logical
constructs in the WHERE (and HAVING) clause.
·
Scalar
Subqueries - standalone queries that
return a single value; they can be used anywhere a scalar value is used.
·
Table
Subqueries - queries nested in the
FROM clause.
A primary key is a field or
combination of fields that uniquely identify a record in a table, so that an
individual record can be located without confusion.
A foreign key (sometimes called a referencing key) is a key used to link two tables together. Typically you take the primary key field from one table and insert it into the other table where it becomes a foreign key (it remains a primary key in the original table).
A foreign key (sometimes called a referencing key) is a key used to link two tables together. Typically you take the primary key field from one table and insert it into the other table where it becomes a foreign key (it remains a primary key in the original table).
20. What is data integrity? Explain constraints?
data integrity
refers to maintaining and assuring the accuracy and consistency of data over its entire life-cycle,[1]
and is an important feature of a database or RDBMS system.
Constraints:
·
NOT NULL
·
UNIQUE
·
PRIMARY KEY
·
FOREIGN KEY
·
CHECK
21.
What is
De-normalization?
De-normalization
is the process of attempting to optimize the performance of a database by
adding redundant data. It is sometimes necessary because current DBMSs
implement the relational model poorly.
De-normalization
is a technique to move from higher to lower normal forms of database modeling
in order to speed up database access.
22.
Can we rewrite sub queries into simple select
statements or with joins?
Yes we can write
using Common Table Expression (CTE). A Common Table Expression (CTE) is an
expression that can be thought of as a temporary result set which is defined
within the execution of a single SQL statement. A CTE is similar to a derived
table in that it is not stored as an object and lasts only for the duration of
the query.
23.
What is Self Join?
Let’s illustrate the need for a self join with an example.
Suppose we have the following table – that is called employee. The employee
table has 2 columns – one for the employee name (called employee_name), and one
for the employee location (called employee_location):
Employee
|
||||||||||||
|
Now, suppose we want to find out which employees are from
the same location as the employee named Joe. In this example, that location
would be New York. What we could do is write a nested SQL query (basically a
query within another query – which is also called a subquery) like this:
SELECT
employee_name
FROM
employee
WHERE
employee_location in
(
SELECT employee_location
FROM
employee
WHERE
employee_name = "Joe")
|
24. What is Cross Join?
The SQL CROSS JOIN produces
a result set which is the number of rows in the first table multiplied by the
number of rows in the second table, if no WHERE clause is used along with CROSS
JOIN. This kind of result is called as Cartesian Product.
25.
List few
advantages of Stored Procedure.
Stored procedure can reduced network traffic and latency,
boosting application performance.
· Stored procedure execution plans can be reused, staying
cached in SQL Server’s memory, reducing server overhead.
· Stored procedures help promote code reuse.
· Stored procedures can encapsulate logic. You can change
stored procedure code without
affecting clients.
· Stored procedures provide better security to your data.
http://java67.blogspot.com/2013/04/10-frequently-asked-sql-query-interview-questions-answers-database.html
http://www.dwbiconcepts.com/tutorial/24-interview-questions/190-top-20-sql-interview-questions-with-answers.html
https://www.codeproject.com/articles/126898/sql-server-how-to-write-a-stored-procedure-in-sql
http://java67.blogspot.com/2013/04/10-frequently-asked-sql-query-interview-questions-answers-database.html
http://www.dwbiconcepts.com/tutorial/24-interview-questions/190-top-20-sql-interview-questions-with-answers.html
https://www.codeproject.com/articles/126898/sql-server-how-to-write-a-stored-procedure-in-sql
Hide Copy Code
CREATE TABLE tbl_Students
(
[Studentid] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[Firstname] [nvarchar](200) NOT NULL,
[Lastname] [nvarchar](200) NULL,
[Email] [nvarchar](100) NULL
)
Insert into tbl_Students (Firstname, lastname, Email)
Values('Vivek', 'Johari', 'vivek@abc.com')
Create Procedure Procedure-name
(
Input parameters ,
Output Parameters (If required)
)
As
Begin
Sql statement used in the stored procedure
End
/*
GetstudentnameInOutputVariable is the name of the stored procedure which
uses output variable @Studentname to collect the student name returns by the
stored procedure
*/
Create PROCEDURE GetstudentnameInOutputVariable
(
@studentid INT, --Input parameter , Studentid of the student
@studentname VARCHAR(200) OUT-- Out parameter declared with the help of OUT keyword
)
AS
BEGIN
SELECT @studentname= Firstname+' '+Lastname FROM tbl_Students WHERE studentid=@studentid
END
/*
This Stored procedure is used to Insert value into the table tbl_students.
*/
Create Procedure InsertStudentrecord
(
@StudentFirstName Varchar(200),
@StudentLastName Varchar(200),
@StudentEmail Varchar(50)
)
As
Begin
Insert into tbl_Students (Firstname, lastname, Email)
Values(@StudentFirstName, @StudentLastName,@StudentEmail)
End
Declare @Studentname as nvarchar(200) -- Declaring the variable to collect the Studentname
Declare @Studentemail as nvarchar(50) -- Declaring the variable to collect the Studentemail
Execute GetstudentnameInOutputVariable 1 , @Studentname output, @Studentemail output
select @Studentname,@Studentemail -- "Select" Statement is used to show the output from Procedure
Declare @NoOfRecord As int;
SET @NoOfRecord =(Select Count(*) from tblCompanyAddress where CompanyID=11065 and AllocationNumber=54567 );
if(@NoOfRecord>0)
select CompanyName,CompanyAddress AS MailingAddress1,CompanyCity AS MailingCity,CompanyZip AS MailingZip,CompanyState AS MailingStateID,ChangeNote
from tblCompanyAddress
where CompanyID=11065 and AllocationNumber=54567
else
select c.CompanyName,c.MailingCity, c.MailingZip,c.MailingStateID,'' AS ChangeNote
from tblcompany c left join States s on c.MailingStateID = s.StateNumber where c.id=11065
Difference between Clustered and Non-Clustered Index
S.No Clustered Non-clustered 1 A clustered index is used to define the order or to sort the table or arrange the data by alphabetical order just like a dictionary. A non-clustered index collects the data at one place and records at another place. 2 It is faster than a non-clustered index. It is slower than the clustered index. 3 It demands less memory to execute the operation. It demands more memory to execute the operations. 4 It permits you to save data sheets in the leaf nodes of the index. It never saves data sheets in the leaf nodes of the index. 5 A single table can consist of a sole cluster index. It can consist of multiple non-clustered indexes. 6 It has the natural ability to store data on the disk. It does not have the natural strength to store data on the disk.
create nonclustered index NIX_FTE_Name
on Student (Name ASC);
sqlselect * from Content where ApproversListData <> ''Trigger
***********************NorthWind Database********************
//delete duplicate rows
with categoryCTE as
(
select *,ROW_NUMBER() over (partition by CategoryName
order by CategoryName) as rownumber from Categories
)
delete from categoryCTE where rownumber>1
WITH CTE AS (
SELECT
Column1,
Column2,
Column3,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY Column1, Column2 ORDER BY (SELECT 0)) AS RowNum
FROM YourTable
)
DELETE FROM CTE WHERE RowNum > 1;
//select N highest
select top 1 * from
(select distinct top 5 *
from Products
order by Price desc
) result
order by Pricehttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=35gjU7pChQk
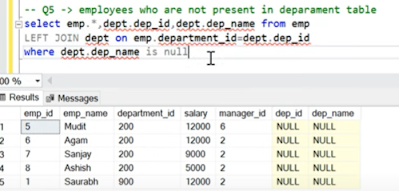

List the employee details whose salary is greater than average salary of their department.
SELECT *
FROM products p
INNER JOIN(SELECT categoryid,Avg(price) price
FROM products
GROUP BY categoryid
) pa
ON p.categoryid = pa.categoryid
WHERE p.price > pa.price
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
GROUP BY column_name(s)
ORDER BY column_name(s);
What is the different between UNION and UNION ALL 2.
Department dId name 1 Marketing 2 Finance 3 Statistics
Student sId name 1 Rashed 2 Jony 3 Mahfuz 4 Rony 5 Mamun 6 Kayes 7 Nishu 8 Mukul 9 Riaz 10 Rubol
StudentDepaermentXref sId dId 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 5 2 6 3
----------------Answer of query1---------------------
--------------------Answer of query2---------------------------
------------------- Answer of Query3---------------------------
-------------------- Answer of query4-------------------
































Subquery or Inner query or a Nested
ReplyDelete