http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/838365/Basic-Csharp-OOPS-Concept
http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/asmabegam/basic-concept-of-oop-in-C-Sharp/
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Data
Hiding
- Encapsulation
- abstraction
- Overloading
- Reusability
It solves the problem in implementation level.
Example:
class A1
{
void hello()
{ Console.WriteLine(“Hello”); }
void hello(string s)
{ Console.WriteLine(“Hello {0}”,s); }
}
It solves the problem in design level itself.
Encapsulation is used for hide the code and data in a single unit to protect the data from the outside the world.
It solves the problem in implementation level.
Feature
|
Interface
|
Abstract class
|
|
Multiple inheritance
|
A class may inherit several interfaces.
|
A class may inherit only one abstract class.
|
|
Default implementation
|
An interface cannot provide any code, just the signature.
|
An abstract class can provide complete, default code
and/or just the details that have to be overridden.
|
|
Access Modfiers
|
An interface cannot have access
modifiers for the subs, functions, properties etc everything is assumed as
public
|
An abstract class can contain
access modifiers for the subs, functions, properties
|
|
Homogeneity
|
If various implementations only share method signatures
then it is better to use Interfaces.
|
If various implementations are of the same kind and use
common behaviour or status then abstract class is better to use.
|
1. another namespace
2. class
3. interface
4. struct
5. enum
6. delegate
Assembly :
An Assembly can contain many namespaces. Assemblies contain MSIL code.
Assemblies are Self-Describing. [e.g. metadata,manifest]
Differences:
1)A namespace is logically groups classes.An assembly is physical grouping of logical units.
2)An Assembly contains one or more namespaces
In other words, generics allow you to write a class or method that can work with any data type.
Looking at first site the The Keyword Sealed & Abstract are contradictory to each other..In simple terms we can Say Answer is NO...
Look the code below
using System;
abstract class A
{
public abstract void Hello();
}
when we will complie the code.. we will get the Compile time Error as below
'A.Hi()' cannot be sealed because it is not an override..
But We can have Sealed methods in abstract class when the abstract class is Dervided class .. for Eg.
using System;
class A
{
public virtual void Hello()
{
Console.WriteLine(" Say Hello");
}
}
abstract class B : A
{
public sealed override void Hello()
{
Console.WriteLine(" Say Hi");
}
}
class C : B
{
}
class Demo
{
public static void Main()
{
C c1 = new C();
c1.Hello();// Output is Say Hi
}
}
Internal is the access modifier of classhttps://dotnetcodr.com/2013/10/17/the-dont-repeat-yourself-dry-design-principle-in-net-part-1/
https://dotnetcodr.com/architecture-and-patterns/
KISS
https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/article/software-design-principles-dry-kiss-yagni/
S O L I D
SOLID are guidelines that can be applied while working on software to remove code smells by causing the programmer to refactor the software's source code until it is both legible and extensible. - Subtypes must be substitutable for their base types.
- Clients should not be forced to depend upon interfaces that they do not use.
- · Many client specific interfaces are better than one general purpose interface
A. High-level modules should not depend on low-level modules. Both should depend on abstractions.
B. Abstractions should not depend upon details. Details should depend upon abstractions.
ersion of
control
|
Dependency
injection
|
It’s a generic term and implemented in several ways
(events, delegates etc).
|
DI is a subtype of IOC and is implemented by constructor
injection, setter injection or method injection.
|
 |
http://mohammadnazmul.blogspot.com/2014/05/solid.html
https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/703634/SOLID-architecture-principles-using-simple-Csharp
Delegate
http://www.tutorialsteacher.com/csharp/csharp-func-delegate http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/8911c4/simple-delegates-with-examples-in-C-Sharp/
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/csharp/csharp_delegates.htm
{
{
GetData("Mahesh");
}
}
public void GetData(string Name)
{
lblName.Text = Name;
}
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
if (!IsPostBack)
{
MyDelegare objMyDelegare = new MyDelegare(GetData);
objMyDelegare("Mahesh");
}
}
public void GetData(string Name)
{
lblName.Text = Name;
}
What is reflection?
Generics
http://tech.priyo.com/tutorial/2014/11/18/26914.html
refer to a feature in C# that allows defining a class or method with type as a parameter.
Generics allow for designing a classes and methods whose types are specified only at the time of declaration and instantiation.
The List<T> collection class is an example for generic class
- Casting is not required for accessing each element in the collection
class Test<T>
{
T _value;
public Test(T t)
{
// The field has the same type as the parameter.
this._value = t;
}
public void Write()
{
Console.WriteLine(this._value);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// Use the generic type Test with an int type parameter.
Test<int> test1 = new Test<int>(5);
// Call the Write method.
test1.Write();
// Use the generic type Test with a string type parameter.
Test<string> test2 = new Test<string>("cat");
test2.Write();
}
}
Output
5
cat
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static List<T> GetInitializedList<T>(T value, int count)
{
// This generic method returns a List with ten elements initialized.
// ... It uses a type parameter.
// ... It uses the "open type" T.
List<T> list = new List<T>();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
list.Add(value);
}
return list;
}
static void Main()
{
// Use the generic method.
// ... Specifying the type parameter is optional here.
// ... Then print the results.
List<bool> list1 = GetInitializedList(true, 5);
List<string> list2 = GetInitializedList<string>("Perls", 3);
foreach (bool value in list1)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
foreach (string value in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
}
Output
True
True
True
True
True
Perls
Perls
Perls
http://www.dotnet-tricks.com/Tutorial/csharp/FU4N141113-Difference-Between-Constant-and-ReadOnly-and-Static.html
const variables can declared in methods ,while readonly fields cannot be declared in methods
class EnumProgram { enum Days { Sun, Mon, tue, Wed, thu, Fri, Sat }; static void Main(string[] args) { int WeekdayStart = (int)Days.Mon; int WeekdayEnd = (int)Days.Fri; Console.WriteLine("Monday: {0}", WeekdayStart); Console.WriteLine("Friday: {0}", WeekdayEnd); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
Monday: 1 Friday: 5
struct
struct Books { public string title; public string author; public string subject; public int book_id; }; public class testStructure { public static void Main(string[] args) { Books Book1; /* Declare Book1 of type Book */ Books Book2; /* Declare Book2 of type Book */ /* book 1 specification */ Book1.title = "C Programming"; Book1.author = "Nuha Ali"; Book1.subject = "C Programming Tutorial"; Book1.book_id = 6495407; /* book 2 specification */ Book2.title = "Telecom Billing"; Book2.author = "Zara Ali"; Book2.subject = "Telecom Billing Tutorial"; Book2.book_id = 6495700; /* print Book1 info */ Console.WriteLine( "Book 1 title : {0}", Book1.title); Console.WriteLine("Book 1 author : {0}", Book1.author); Console.WriteLine("Book 1 subject : {0}", Book1.subject); Console.WriteLine("Book 1 book_id :{0}", Book1.book_id);
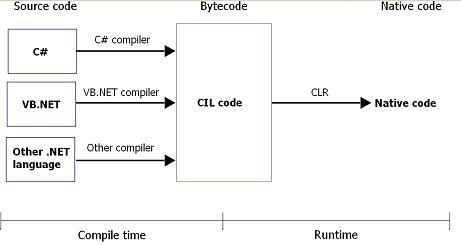
http://www.herongyang.com/C-Sharp/Intermediate-Language-Compile-and-Run-C-Sharp-Program.html
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=umfhcv-UxxQ&list=PLiceGnDCE4Xbtd2y-i8v4PfLp47SX6MkV&index=2
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sx2U8kQ3DLM&list=PLKiZXxQe7OiC2RzvzDCKmSn-7ZdsXLeSF
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_pgUO1iz8Ps&t=9s
Extension Methods
Scoped (সীমিত)
ব্যবহার: একটি HTTP request এর জন্য একটি instance তৈরি হয় এবং সেই request-এর মধ্যে যতবার দরকার হয়, একই instance ব্যবহার হয়।
উদাহরণ:
DbContextসাধারণত Scoped হিসেবে রেজিস্টার করা হয়, যাতে একটি request-এর মধ্যে একই database connection ব্যবহার হয়।কখন ব্যবহার করবেন:
যখন সার্ভিসটি request-specific data নিয়ে কাজ করে।কোড উদাহরণ:
3️⃣ Singleton (একক)
ব্যবহার: অ্যাপ্লিকেশন চালু হওয়ার সময় একটি instance তৈরি হয় এবং পুরো অ্যাপ্লিকেশন জুড়ে সেটি ব্যবহার হয়।
উদাহরণ:
Logging service বা configuration service সাধারণত Singleton হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।কখন ব্যবহার করবেন:
যখন সার্ভিসটি shared state বা global configuration নিয়ে কাজ করে এবং বারবার নতুন instance দরকার হয় না।কোড উদাহরণ:
📊 তুলনামূলক চার্ট
| Lifecycle | Instance তৈরি হয় | Reuse হয় | উপযুক্ত ক্ষেত্র |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transient | প্রতিবার | না | Stateless service |
| Scoped | প্রতি request | হ্যাঁ | Request-specific service |
| Singleton | একবার | হ্যাঁ | Global/shared service |
ধরুন আপনি একটি ই-কমার্স ওয়েবসাইট তৈরি করেছেন যেখানে একজন ব্যবহারকারী একটি HTTP request-এর মাধ্যমে তার shopping cart-এ পণ্য যোগ করে।
✅ কেন Scoped?
- একটি request-এর মধ্যে cart-এর অবস্থা (state) ধরে রাখতে হয়
- একই request-এর মধ্যে বারবার একই instance ব্যবহার করতে হয়
- performance এবং consistency বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে
🧠 বাস্তব চিত্র:
যখন একজন ব্যবহারকারী checkout পেজে যায়, তখন CartService instance তৈরি হয় এবং সেই request-এর মধ্যে যতবার cart data দরকার হয়, একই instance ব্যবহার হয়। এতে করে cart-এর অবস্থা ঠিক থাকে এবং বারবার নতুন instance তৈরি করতে হয় না।
📊 তুলনামূলক বাস্তব উদাহরণ
| Scenario | Lifecycle | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| ইমেইল পাঠানো | Transient | Stateless, প্রতি বার নতুন instance দরকার |
| Checkout পেজে cart পরিচালনা | Scoped | Stateful, request-specific instance দরকার |
| Logging service | Singleton | পুরো অ্যাপ্লিকেশনে একই instance দরকার |
Transient objects are always different; a new instance is provided to every controller and every service.
Scoped objects are the same within a request, but different across different requests.
Singleton objects are the same for every object and every request.
https://www.dofactory.com/code-examples/csharp/service-lifetimes
In C#, records and classes look similar but serve different purposes. Knowing when to use each can improve performance, organization, and readability of your code.
🔹Classes are ideal for objects that can change state.
- Best for: Database entities, domain models, objects that need state changes.
🔹Records are immutable by default and compared by value.
- Best for: DTOs, API response models, objects that shouldn't be modified.
✅ When to Use Records?
- Immutable objects
- Value-based comparison
- DTOs and API responses
❌ When to Avoid?
- If you need mutable objects
- If using Entity Framework, which requires mutability
Have you used records in your projects?
𝐒𝐮𝐦𝐦𝐚𝐫𝐲:
- 𝐈𝐄𝐧𝐮𝐦𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐛𝐥𝐞<𝐓>: Read-only, used for iteration.
- 𝐈𝐂𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧<𝐓>: Adds collection manipulation (add/remove).
- 𝐈𝐋𝐢𝐬𝐭<𝐓>: Supports indexing and collection manipulation.
🔍 𝐏𝐮𝐫𝐩𝐨𝐬𝐞: It represents a read-only forward-only collection of items.
🛠️ 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐦𝐨𝐧 𝐔𝐬𝐞: Ideal for iterating through a collection using a foreach loop.
🚫 𝐂𝐚𝐧𝐧𝐨𝐭 𝐦𝐨𝐝𝐢𝐟𝐲: It doesn't allow adding, removing, or modifying elements.
📖 𝐄𝐱𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞: LINQ queries often return IEnumerable.
2. 𝐈𝐂𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧<𝐓>
💼 𝐏𝐮𝐫𝐩𝐨𝐬𝐞: Extends IEnumerable with additional features like adding, removing, and checking the size of a collection.
➕ 𝐒𝐮𝐩𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭𝐬 𝐀𝐝𝐝/𝐑𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐯𝐞: Unlike IEnumerable, you can modify the collection.
🏗️ 𝐔𝐬𝐞 𝐰𝐡𝐞𝐧: You need collection manipulation without requiring indexing.
3. 𝐈𝐋𝐢𝐬𝐭<𝐓>
📚 𝐏𝐮𝐫𝐩𝐨𝐬𝐞: Extends ICollection with the ability to access elements by index.
🔢 𝐒𝐮𝐩𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭𝐬 𝐈𝐧𝐝𝐞𝐱𝐢𝐧𝐠: You can access and modify elements using an index, like an array.
⚡𝐔𝐬𝐞 𝐰𝐡𝐞𝐧: You need direct access to elements via indexing along with modification capabilities.
4. 𝐋𝐢𝐬𝐭<𝐓>
🎯 𝐏𝐮𝐫𝐩𝐨𝐬𝐞: A concrete implementation of IList.
🔥 𝐌𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐅𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞𝐬: Offers all the functionalities of IList, ICollection, and IEnumerable.
🌱 𝐃𝐲𝐧𝐚𝐦𝐢𝐜 𝐒𝐢𝐳𝐞: Automatically resizes as elements are added or removed.
⚙️ 𝐔𝐬𝐞 𝐰𝐡𝐞𝐧: You need a resizable collection with full manipulation and indexing support.




















































No comments:
Post a Comment