What are microservices?
Microservices - also known as the microservice architecture - is an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of services that are
- Highly maintainable and testable
- Loosely coupled
- Independently deployable
- Organized around business capabilities
- Owned by a small team
Installing on Windows : https://www.rabbitmq.com/install-windows.html
C:\Program Files\RabbitMQ Server\rabbitmq_server-3.12.11\sbin>rabbitmq-plugins.bat list✅ কিভাবে কাজ করে (Bangla)
RabbitMQ-এর কাজের ধাপগুলো সহজভাবে নিচে দেওয়া হলো:
-
Producer
- Producer হলো সেই অ্যাপ্লিকেশন যা বার্তা (message) তৈরি করে এবং RabbitMQ-তে পাঠায়।
- Producer বার্তাটি একটি Queue-তে পাঠায়।
-
Queue
- Queue হলো একটি বাফার যেখানে বার্তাগুলো জমা থাকে যতক্ষণ না Consumer সেগুলো গ্রহণ করে।
- এটি বার্তাগুলোকে অস্থায়ীভাবে ধরে রাখে।
-
Consumer
- Consumer হলো সেই অ্যাপ্লিকেশন যা Queue থেকে বার্তা গ্রহণ করে এবং প্রসেস করে।
- Consumer বার্তা পাওয়ার পর সেটি প্রিন্ট করতে পারে, ডাটাবেসে রাখতে পারে, বা অন্য কোনো কাজ করতে পারে।
-
Connection এবং Channel
- Producer এবং Consumer RabbitMQ সার্ভারের সাথে Connection তৈরি করে।
- Connection-এর ভিতরে Channel থাকে, যা আসল কাজ করে (Queue declare, message publish, consume)।
-
Flow
- Producer → Queue → Consumer
- Producer বার্তা পাঠায় → Queue বার্তাটি ধরে রাখে → Consumer বার্তাটি পড়ে এবং প্রসেস করে।
RabbitMQ-এর মূল সুবিধা:
- Decoupling: Sender এবং Receiver একসাথে চলতে হবে না।
- Reliability: বার্তা হারিয়ে যায় না (acknowledgment এবং persistence সাপোর্ট করে)।
- Scalability: অনেক বেশি লোড হ্যান্ডেল করতে পারে।
Copilot said:
Here you go, Mohammad!
50+ Azure Service Bus Interview Questions and Answers (Bangla + English) — simple, clear, side‑by‑side.
Perfect for interviews and revision.
✅ Azure Service Bus Interview – 50+ Questions & Answers
(Bangla + English side-by-side)
1. What is Azure Service Bus?
EN: Azure Service Bus is a fully managed enterprise message broker that enables reliable communication between applications using queues and topics.
BN: Azure Service Bus হলো একটি fully managed enterprise message broker, যা queues এবং topics ব্যবহার করে অ্যাপ্লিকেশনগুলোর মধ্যে নির্ভরযোগ্য যোগাযোগ নিশ্চিত করে।
2. Why do we use Azure Service Bus?
EN: It decouples systems, supports asynchronous communication, ensures reliability, and handles spikes in traffic.
BN: এটি সিস্টেমগুলোকে decouple করে, asynchronous যোগাযোগ সাপোর্ট করে, নির্ভরযোগ্যতা নিশ্চিত করে এবং হঠাৎ লোড বৃদ্ধি ম্যানেজ করে।
3. What are the key components of Service Bus?
EN: Namespace, Queues, Topics, Subscriptions, Filters, SAS Policies.
BN: Namespace, Queue, Topic, Subscription, Filter, SAS Policy।
4. What is a Service Bus Queue?
EN: A point‑to‑point messaging system (sender → queue → receiver).
BN: একটি point‑to‑point মেসেজিং সিস্টেম (sender → queue → receiver)।
5. What is a Topic?
EN: A publish‑subscribe messaging system where multiple receivers can subscribe.
BN: Publish‑subscribe মডেল যেখানে একাধিক subscriber মেসেজ পায়।
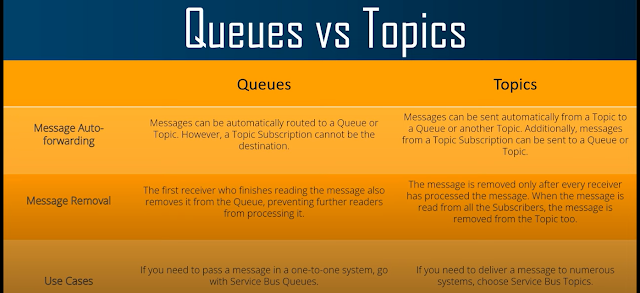
6. Difference between Queue and Topic?
EN: Queue = Single Consumer.
Topic = Multiple Subscribers.
BN: Queue = এক consumer পায়
Topic = একাধিক subscription পায়।
7. What is a Dead Letter Queue (DLQ)?
EN: A sub-queue where failed messages are stored.
BN: যেসব মেসেজ প্রসেস করা যায় না, সেগুলো রাখার জন্য DLQ ব্যবহার হয়।
8. Why do messages go to DLQ?
EN: TTL expire, max delivery count exceeded, processing errors.
BN: TTL শেষ হওয়া, বারবার প্রসেস ব্যর্থ হওয়া, errors।
9. What is Message TTL?
EN: A time limit after which a message becomes invalid.
BN: নির্দিষ্ট সময় পর মেসেজ invalid হয়ে যায়।
10. What is Max Delivery Count?
EN: Number of times Service Bus retries delivering a message.
BN: কতবার retry করে deliver করার চেষ্টা করবে।
11. What are Sessions?
EN: Used for ordered message processing.
BN: Ordered মেসেজ প্রসেস করার জন্য Session ব্যবহার করা হয়।
12. What is Partitioning?
EN: Spreads messages across multiple brokers for high throughput.
BN: Load ভাগ করে throughput বাড়ায়।
13. What is Duplicate Detection?
EN: Service Bus prevents duplicate messages within a time window.
BN: নির্দিষ্ট সময়ে duplicate মেসেজ ব্লক করে।
14. What is PeekLock mode?
EN: A message is locked for a specific receiver but not deleted.
BN: Receiver মেসেজ পড়তে পারে কিন্তু ডিলিট হয় না, locked থাকে।
15. What is Receive and Delete mode?
EN: Deletes message immediately after reading.
BN: মেসেজ পড়ার সাথে সাথেই ডিলিট হয়ে যায়।
16. Which mode ensures no message loss?
EN: PeekLock
BN: PeekLock
17. What is Auto-Forwarding?
EN: Automatically forwards messages from one queue/topic to another.
BN: একটি queue/topic থেকে আরেকটিতে মেসেজ অটো ফরওয়ার্ড করে।
18. What is Scheduled Messaging?
EN: Sending messages to be processed at a future time.
BN: ভবিষ্যতে নির্দিষ্ট সময়ে মেসেজ পাঠানো।
19. What is Deferring a message?
EN: Temporarily postponing processing.
BN: মেসেজ প্রসেস কিছু সময়ের জন্য পিছিয়ে দেওয়া।
20. What is a Subscription Filter?
EN: Rules to decide which message a subscription will receive.
BN: কোন মেসেজ কোন subscription পাবে তা নির্ধারণের নিয়ম।
21. Types of Filters?
EN: SQL Filter, Correlation Filter
BN: SQL Filter, Correlation Filter
22. What is Namespace?
EN: A container for queues, topics, subscriptions.
BN: Queue, Topic, Subscription রাখার কন্টেইনার।
23. What is Shared Access Signature (SAS)?
EN: Token-based authentication method.
BN: Token ভিত্তিক authentication পদ্ধতি।
24. What is AMQP?
EN: Advanced Message Queuing Protocol used for efficient messaging.
BN: কার্যকর মেসেজিংয়ের জন্য ব্যবহৃত একটি প্রোটোকল।
25. Difference between AMQP and HTTPS?
EN: AMQP = faster, duplex.
HTTPS = simpler, slower.
BN: AMQP = দ্রুত, দুই‑দিকের যোগাযোগ
HTTPS = সহজ, ধীরগতি।
26. What is Prefetch Count?
EN: Number of messages fetched in advance.
BN: আগেই একসাথে কিছু মেসেজ টেনে আনা।
27. What is Message Lock Duration?
EN: Duration a message remains locked in PeekLock.
BN: PeekLock‑এ মেসেজ কত সময় locked থাকবে।
28. Can a Topic have multiple subscriptions?
EN: Yes.
BN: হ্যাঁ।
29. Can a Queue have multiple receivers?
EN: Yes, but each message goes to only one.
BN: রিসিভার একাধিক হতে পারে, কিন্তু মেসেজ একটির কাছে যাবে।
30. What is Geo-Disaster Recovery?
EN: Cross-region failover.
BN: Region-wide সমস্যায় backup region এ স্যুইচ।
31. Standard vs Premium differences?
EN:
- Premium = Dedicated compute, higher throughput
- Standard = Shared infrastructure
BN: - Premium = Dedicated resources, বেশি throughput
- Standard = Shared resources
32. Can Service Bus trigger Azure Functions?
EN: Yes.
BN: হ্যাঁ।
33. What is Dead-letter Reason?
EN: Explains why message went to DLQ.
BN: কেন DLQ‑এ গেল তা দেখায়।
34. Maximum message size?
EN:
- Standard: 256 KB
- Premium: 1 MB
BN: - Standard: 256 KB
- Premium: 1 MB
35. Is FIFO supported?
EN: Yes, via Sessions.
BN: হ্যাঁ, Session ব্যবহার করে।
36. What is Service Bus Explorer?
EN: Tool to manage and test Service Bus.
BN: Service Bus টেস্ট ও ম্যানেজ করার টুল।
37. What are Message Properties?
EN: Custom key-value meta-data.
BN: কাস্টম কী-ভ্যালু তথ্য।
38. Queues vs Storage Queues?
EN:
Service Bus = enterprise, ordering, sessions
Storage Queue = simple, cheap
BN:
Service Bus = এন্টারপ্রাইজ, ordering সহ
Storage Queue = সহজ, সস্তা
39. What is Auto-Complete?
EN: Auto deletes message after function completes successfully.
BN: Function সফল হলে মেসেজ নিজে ডিলিট হয়।
40. What is DeadLetter() API?
EN: Manually moves message to DLQ.
BN: মেসেজ manually DLQ‑তে পাঠানো।
41–50: Rapid-fire (Bangla + English)
Batch Receive?
EN: Receive multiple messages at once.
BN: একসাথে অনেক মেসেজ রিসিভ করা।Atomic Transactions?
EN: Multiple operations as a single unit.
BN: একাধিক কাজকে একসাথে atomic ভাবে চালানো।Ordering guarantee?
EN: Only with sessions.
BN: শুধু sessions‑এ।Can we send large files?
EN: Not recommended; use blob + reference.
BN: বড় ফাইল নয়; blob এ রেখে রেফারেন্স পাঠান।Poison Messages?
EN: Messages that always fail processing.
BN: বারবার error হওয়া মেসেজ।Auto Delete on Idle?
EN: Deletes unused subscriptions after inactivity.
BN: দীর্ঘ সময় ব্যবহার না হলে subscription ডিলিট হয়।What is CorrelationId?
EN: Used to match related messages.
BN: related মেসেজ track করতে ব্যবহৃত।Can Service Bus work offline?
EN: No (cloud service).
BN: না (cloud service)।What is Message Deferral Id?
EN: ID needed to retrieve deferred message.
BN: deferred মেসেজ ফেরত আনার জন্য আইডি।How to reprocess DLQ messages?
EN: Read and send to main queue again.
BN: DLQ থেকে পড়ে আবার main queue‑তে পাঠানো।